AI and games have been fundamentally intertwined from their inception, pushing one another to new frontiers. Games, with their precise rules and narrow subdomains, provide the perfect arena for game AI to excel. This blog offers a glimpse into one of our attempts at creating a multi-agent game and explores the complexities involved in designing a multi-agent system in the world of AI in gaming.
The Game
Let’s talk about the game we’ve built, called "Matrix". It’s a blockchain-based multiplayer game that helps players learn new languages through fun, mission-based challenges drawn from everyday life. While creating the game, we delved into the intricacies of game AI to make AI agent responses more human-like and explored how to make interactions feel more natural.
Through this journey, we identified four main processes that make any interaction more human-like:
- ● Augmenting movements and natural interactions
- ● Augmenting emotions
- ● Augmenting memory
- ● Augmenting personas

Augmenting Movements and Natural Interactions
How Simple Games Augment Natural Movements and Interactions
Early game AI implementations were relatively simple, combining fixed patterns with behavior changes based on player actions. A common method used is the finite state machine (FSM), which divides the game into various states, each with specific rules. The AI switches between these states depending on the player’s actions.
For example, in Pac-Man, enemy behaviors follow these four states:
- ● Wander around the maze
- ● Chase Pac-Man
- ● Return to their base
- ● Run away from Pac-Man
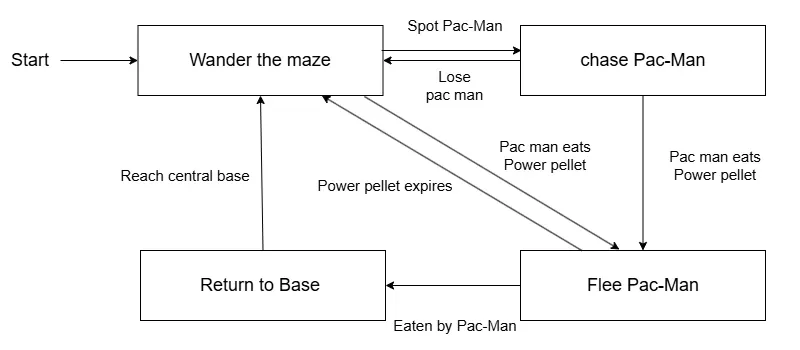
Our Approach of AI in Gaming
In gaming, non-player characters (NPCs) act as agents that interact with players. We’ve implemented a hybrid state machine where NPC behavior is influenced not only by fixed instructions but also by real-time decisions made by the AI agent during interactions.
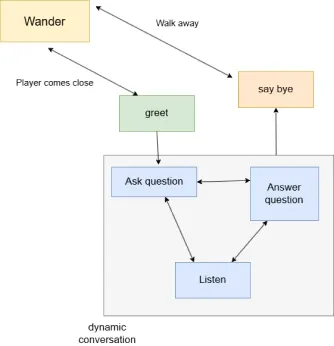
Augmenting Emotional Interactions with AI in Gaming
Emotions play a vital role in human interactions, influencing decision-making and relationships. In the realm of AI in gaming, simulating emotions allows game AI to feel more relatable and human.
We treat emotions as dynamic, changing based on interactions and experiences. For example, how we feel can be influenced by what we experience in our day-to-day lives—whether it's a positive event like meeting a friend or a negative event like an argument. Our emotions also shift based on how we communicate with people, how they treat us, and the overall mood of our interactions. So, instead of thinking of emotions as permanent, we see them as something that can change, grow, or shift depending on what's happening in our lives.
Our approach includes simulating basic emotions like happiness, sadness, anger, and more, updating them after each interaction using detailed prompts. For example:
"Based on the details of the last conversation, please analyze and determine what emotion best describes how the person might be feeling. Consider factors like their tone, the context of the conversation, and any emotional cues in their words.
For example, if the conversation was about a recent achievement, the person might be feeling happy or proud. If they discussed something challenging or stressful, they might be feeling anxious or frustrated. Please provide the most likely emotion based on this information.
Examples:
- ● If the person talked about a fun day with friends, the emotion could be joy.
- ● If they mentioned a stressful situation at school or work, the emotion might be anxiety.
- ● If they shared something sad, like losing a pet, the emotion could be sadness.
the past conversation is [past_conversation] return the most likely emotion"
Augmenting Memory in Gaming with Advanced AI Techniques
Memory is essential for personalizing interactions in gaming. Game AI with memory can recall past interactions, making conversations more engaging and connected.
In "Matrix", we treat memory as something that changes based on past interactions. For example, how the AI agent responds to a player can depend on what they talked about before, making the conversation feel more connected and relevant. By keeping a record of past interactions, the AI agent can refer back to these memories, creating a more immersive AI in gaming experience.
To do this, we use a prompt:
"Based on the last conversation and past interactions with the player, please come up with a topic for the next interaction that builds on what was discussed before. Think about the player's interests and any unresolved topics or questions.
For example, if the player mentioned a hobby, the AI agent might ask about recent developments in that hobby. If there was a challenging situation discussed, the AI agent might check in to see how things have progressed. Please provide a unique and engaging topic for the next interaction based on this information."
Whenever the AI agent and player interact again, the AI agent remembers previous conversations to make the interaction better. We have added multiple prompts to create new and interesting topics for each interaction.
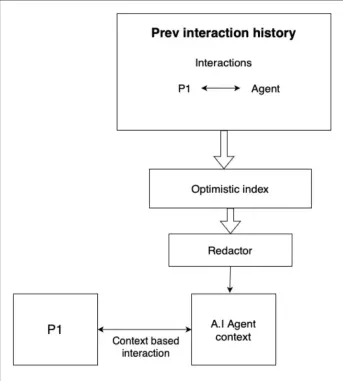
Here's how it goes:
- ● When the player and the AI agent talk, their conversations are saved in a database.
- ● In the future, when the AI agent meets the player again, the AI agent can look up these past conversations.
- ● Some private details from these past chats are removed for privacy.
- ● The remaining conversation info is sent to a large language model (LLM).
- ● Using this info, the LLM helps the AI agent talk to the player with context from their previous interactions, making the conversation feel more connected and personal.
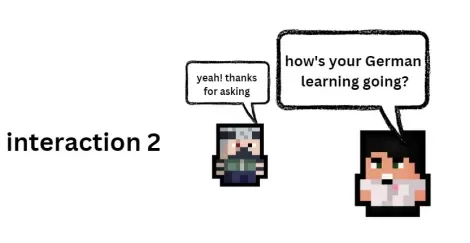
Sample Scenario
Here's an example of how the AI agent (the character in the white dress) interacts with the player (the character on the left). The AI agent remembers what the player talked about before, like their interests and conversations, and stores this information in a database. Later in the game, when the player talks to the AI agent again (like in the second interaction), the AI agent uses this memory to continue the conversation with context from the previous interaction.

Augmenting Persona with AI to Create Dynamic Characters
A persona is a detailed and made-up character profile that represents a specific type of person.
Beliefs, occupation, interests, and lifestyles are some of the things that define a person's persona. We have saved the personas of each person, and any reply generated from the LLM request goes through the persona to update the sentence in their unique style.
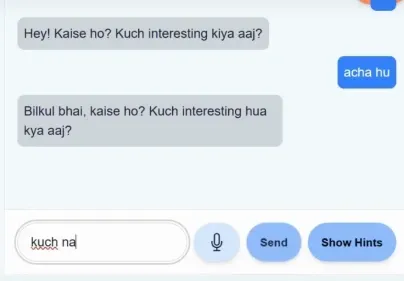
The following is a sample interaction:
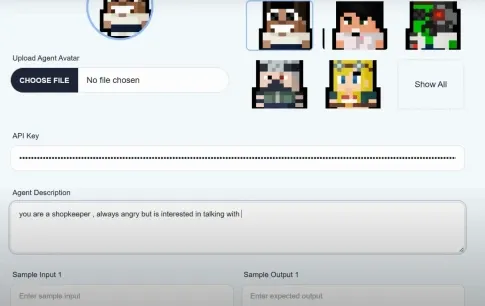
Here's the settings page where you can create an agent with a unique persona. You can describe the agent's occupation, interests, and how they'll interact with people.
The sample input and output also serve as a guide to help the model understand how to reply to anyone.
Creating a multi-agent game like "Matrix" has been a fascinating journey that has deepened our understanding of how AI can enhance human-like interactions in gaming. By focusing on augmenting movements, emotions, memory, and personas, we’ve developed AI agents that react to players and adapt to their behaviors, creating a more immersive and personalized experience. Ultimately, the goal is to create worlds where AI agents are not just programmed to follow patterns, but to truly understand and respond to players in ways that feel real and authentic.
If you're curious about how intelligent agents can transform gaming experiences or want to learn more about our game "Matrix," get in touch with Random Walk today. We're here to answer your questions and collaborate on innovative gaming solutions!