Randomwalk Blogs
All Of Our Thoughts, InOne Place
Randomwalk Blogs
All Of Our Thoughts, In
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an open, vendor-neutral standard for connecting AI models to external data and tools. In effect, MCP acts like a web API built for LLMs. Developers can define Resources (data endpoints) and Tools (callable functions) that the AI can access during a conversation. For example, an MCP server might expose a database as a resource or a function to query that database as a tool.

In the ever - evolving landscape of AI development, Langflow emerges as a game changer. It is an open source, Python powered framework designed to simplify the creation of multi agent and retrieval augmented generation (RAG) applications.






In the UAE, your business is already state-of-the-art. You've invested in top-tier VMS platforms like Genetec and Milestone. You're leveraging the power of AWS and Azure AI. You have the best security "engine" money can buy.




Managing thousands of distributed computing devices, each handling critical real-time data, presents a significant challenge: ensuring seamless operation, robust security, and consistent performance across the entire network. As these systems grow in scale and complexity, traditional monitoring methods often fall short, leaving organizations vulnerable to inefficiencies, security breaches, and performance bottlenecks. Edge system monitoring emerges as a transformative solution, offering real-time visibility, proactive issue detection, and enhanced security to help businesses maintain control over their distributed infrastructure.





What happens when a business recognizes the potential of AI but feels uncertain about where to start? Adopting AI can feel daunting for many companies that are juggling growth ambitions with limited resources. This is a story of a mid-sized manufacturing firm, brimming with ambitions for growth, yet feeling increasingly adrift in a sea of digital disruption. They recognized the immense potential of AI but were hampered by a lack of understanding and a clear path forward. Their journey, much like that of many other organizations, illustrates the transformative power of a strategic approach to AI adoption, driven by a strong foundation of AI readiness.


AI. It’s not just a buzzword anymore; it's a business imperative. Every company is scrambling to harness its potential, promising transformative changes, from customer interactions to supply chain efficiencies. And while the hype is real, so is the reality: most AI projects are failing to deliver. Yes, you heard that right. We're not talking small stumbles here; we're talking about a silent epidemic of stalled projects, wasted investments, and frustrated teams. Are you ready to face the truth?



Artificial intelligence is entering a new phase moving beyond conversational responses and into autonomous action. OpenAI’s newly released Agents SDK is at the center of this shift, giving developers the ability to build intelligent agents that can reason, plan, use tools, execute tasks, manage state, and interact with UI components.

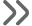
In the digital era, the way people are seen in photos and videos has a huge impact—from memorable movie moments to everyday tools like facial recognition or security checks.




Join leading organizations that trust Randomwalk.ai to power their AI-driven transformation.